Journaling is one of the most accessible and transformative self-care practices. By writing down thoughts, emotions, and reflections, individuals gain clarity, reduce stress, and nurture mental wellness. This guide explores journaling as a holistic tool for self-care, offering evidence-based strategies, real-life examples, and practical techniques for beginners and advanced writers alike.
Introduction
In an age where stress, anxiety, and burnout are increasingly common, self-care has become more than just a buzzword—it’s a necessity. Among the many tools available, journaling stands out as a practice that requires no special training or equipment, yet delivers profound benefits. Whether through structured prompts or free-flowing writing, journaling allows people to slow down, process emotions, and build resilience.
Journaling for self-care is not simply about documenting events; it’s about creating a safe space where you can explore your inner world without judgment. From reducing mental clutter to improving problem-solving skills, journaling supports holistic well-being by nurturing the mind, body, and spirit.
Why Journaling Works as a Self-Care Practice
Mental Benefits
- Encourages emotional release and reduces anxiety.
- Promotes mindfulness by focusing on the present moment.
- Helps process unresolved emotions and trauma.
- Strengthens memory and cognitive processing.
Emotional Benefits
- Builds self-awareness and emotional intelligence.
- Encourages positive self-talk and gratitude.
- Reduces feelings of loneliness by providing a safe outlet.
Physical Benefits
- Studies show journaling can lower blood pressure and strengthen the immune system.
- By reducing stress hormones, journaling contributes to better sleep and overall health.
Real-Life Example:
Anna, a college student, began journaling during exam season. Writing down her worries before bed helped her reduce racing thoughts and improved her sleep quality. Over time, journaling became her go-to method for managing academic stress.
Different Types of Journaling for Self-Care
Free Writing (Stream of Consciousness)
Write continuously for a set period without worrying about grammar or structure. This method clears mental clutter and allows hidden thoughts to surface.
Gratitude Journaling
List three to five things you’re grateful for daily. Gratitude shifts focus from what’s lacking to what’s abundant, boosting positivity.
Reflective Journaling
Reflect on daily experiences, lessons, or emotions. This type helps in processing life events with greater perspective.
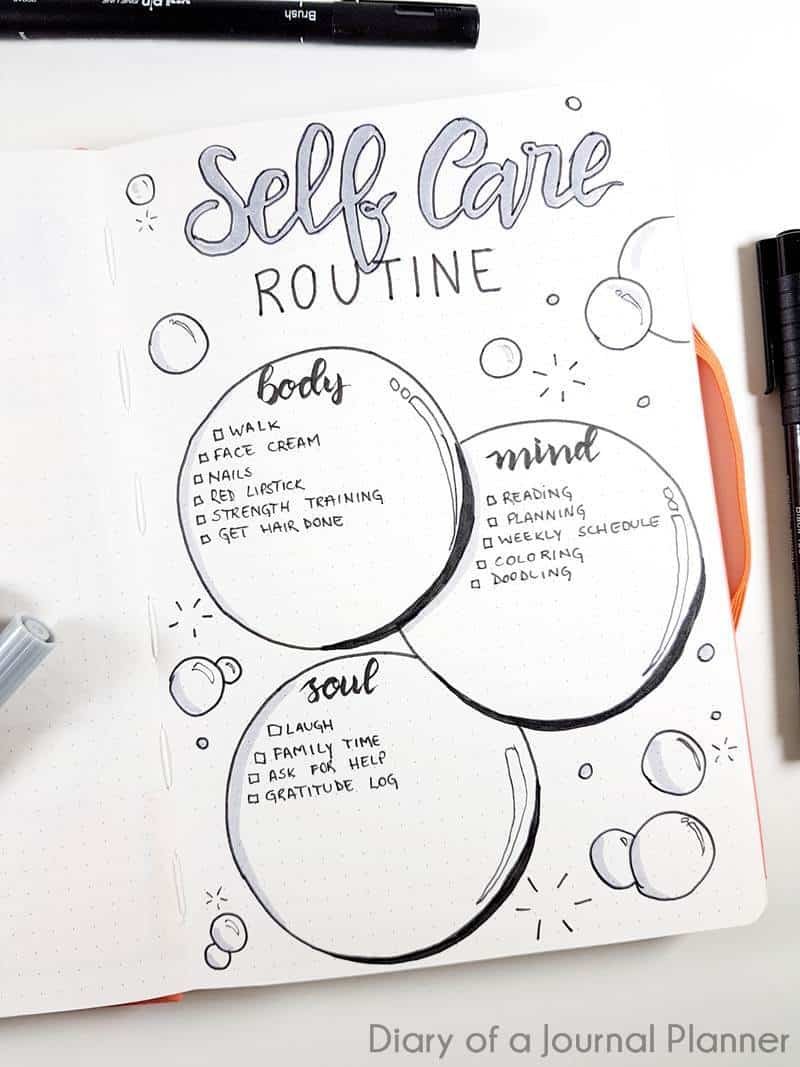
Bullet Journaling
A combination of planning and journaling, bullet journaling helps organize tasks while allowing creative self-expression.
Affirmation Journaling
Write down positive affirmations daily to reframe negative self-beliefs and cultivate confidence.
Art Journaling
Blend words with sketches, doodles, or colors to express emotions visually when words alone aren’t enough.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Start Journaling for Self-Care
- Choose Your Medium
- Traditional notebook or digital apps like Daylio, Journey, or Notion.
- Pick a Time
- Morning journaling for clarity or evening journaling for reflection.
- Create a Comfortable Space
- A quiet corner with minimal distractions fosters consistency.
- Set Realistic Goals
- Start with 5–10 minutes a day to avoid overwhelm.
- Use Prompts if Stuck
- Example prompts:
- “What am I proud of today?”
- “What emotion am I carrying right now?”
- “What do I need to let go of?”
- Example prompts:
- Practice Non-Judgment
- Allow words to flow freely without worrying about perfection.
Real-Life Scenarios of Journaling in Action
- Coping with Grief: After losing her father, Maya used journaling as a way to process memories, express sorrow, and slowly rebuild her emotional strength.
- Managing Burnout: James, a corporate executive, adopted reflective journaling during high-stress projects. Writing helped him identify triggers and restructure his work-life balance.
- Improving Relationships: Writing letters (not sent) helped Rachel manage unresolved anger toward her partner, leading to healthier communication.
How Journaling Supports Other Self-Care Practices
- Mindfulness: Journaling pairs well with meditation by increasing awareness of recurring thoughts.
- Therapy: Many therapists recommend journaling between sessions to track progress.
- Fitness & Nutrition: Food and exercise journals promote accountability.
- Spiritual Practices: Reflective or gratitude journaling deepens spiritual awareness.
Common Challenges in Journaling and How to Overcome Them
- Writer’s Block: Use prompts, lists, or simply describe your environment to get started.
- Consistency Issues: Set reminders or tie journaling to an existing habit (like morning coffee).
- Fear of Exposure: Use password-protected apps or keep journals in a safe place.
- Perfectionism: Remember, journaling is for you, not for public consumption.
Long-Term Benefits of Journaling
- Improved problem-solving skills.
- Greater sense of resilience in facing life challenges.
- Enhanced creativity through regular self-expression.
- Strengthened self-identity by tracking growth over time.
- Reduced emotional reactivity and better regulation of mood.
Case Study:
A study published in Advances in Psychiatric Treatment highlighted that expressive writing significantly lowered symptoms of depression in participants after just a few weeks.
10 FAQs on Journaling for Self-Care
1. How often should I journal for self-care?
Journaling daily provides the best results, but even a few times a week can be effective. Consistency matters more than duration. By setting aside 5–10 minutes a day, you create a habit of reflection that gradually reduces stress and promotes clarity. The key is to view journaling as a supportive ritual rather than a chore.
2. Can journaling replace therapy?
Journaling is a powerful tool, but it is not a substitute for professional therapy. Instead, it complements therapeutic work by helping individuals track emotions, identify triggers, and process sessions. Many therapists encourage patients to journal between visits. It provides insights that enhance therapy’s effectiveness while offering immediate relief between appointments.
3. What should I write about when I feel stuck?
When stuck, try prompts such as “What made me smile today?” or “What challenges did I face and how did I handle them?” You can also list emotions, write affirmations, or even doodle. The goal is not perfection but expression. Over time, writing flows naturally as your mind becomes comfortable with the process.
4. Is digital journaling as effective as writing on paper?
Yes, both are effective. Some people find handwriting more personal and therapeutic, while others prefer digital formats for convenience and privacy. Apps can provide reminders and allow multimedia journaling. The medium you choose should match your lifestyle and comfort level, ensuring consistency rather than forcing a single method.
5. Can journaling really help with anxiety and depression?
Yes, research shows journaling reduces stress hormones, improves mood, and promotes cognitive restructuring. Writing down anxious thoughts helps externalize them, making them feel less overwhelming. For depression, journaling provides perspective and encourages problem-solving. It’s not a cure but a supportive tool that improves mental resilience when practiced regularly.
6. How can journaling improve my self-esteem?
By recording achievements, strengths, and positive affirmations, journaling reinforces self-worth. Reflecting on past successes also builds confidence. Over time, writing shifts focus from failures to growth, reframing self-perception positively. Even small victories noted daily—such as finishing tasks or handling stress—contribute to a stronger self-image and greater overall confidence.
7. Is it okay to journal only when I feel overwhelmed?
Yes, journaling when overwhelmed is helpful, but regular practice offers deeper benefits. Writing during calm moments builds awareness and resilience before stress escalates. Occasional writing provides relief, but consistent journaling develops long-term habits of mindfulness, gratitude, and reflection that prevent emotional buildup and strengthen your coping mechanisms.
8. What’s the best time of day to journal?
There’s no universal best time—it depends on your goals. Morning journaling clears the mind and sets intentions for the day. Evening journaling helps reflect, release stress, and improve sleep. Some people even journal twice a day. Experiment with both to discover when journaling aligns best with your routine and mood.
9. How private should my journal be?
A journal is deeply personal, so privacy is essential. Whether it’s a locked drawer, password-protected app, or coded writing, ensure your journal feels safe. Knowing your words are secure encourages honesty and openness. The more candid you are, the more therapeutic journaling becomes. Treat it as your confidential space of self-expression.
10. How soon can I expect results from journaling?
Many people notice reduced stress and improved clarity within a few weeks of consistent journaling. However, deeper emotional shifts and self-awareness may take months. Journaling is a long-term practice rather than a quick fix. The key is patience and persistence—like physical exercise, results compound with time and dedication.
Conclusion
Journaling for self-care is a transformative practice that empowers individuals to take charge of their mental and emotional well-being. By making journaling a consistent habit, you create a personal sanctuary for reflection, growth, and healing. Whether through gratitude lists, free writing, or reflective entries, journaling offers both immediate relief and long-term resilience.